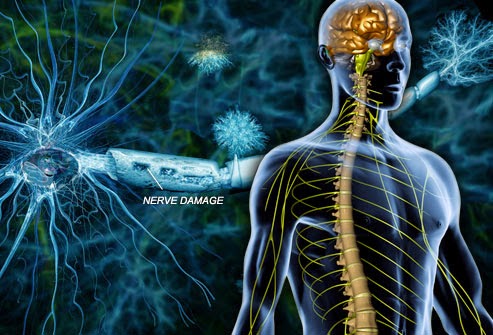
Multiple sclerosis (MS), also known as disseminated sclerosis or encephalomyelitis disseminata, is an inflammatory disease in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged.
This damage disrupts the ability of parts of the nervous system to communicate, resulting in a wide range of signs and symptoms including physical, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. MS takes several forms, with new symptoms either...
occurring in isolated attacks (relapsing forms) or building up over time (progressive forms) Between attacks, symptoms may disappear completely; however, permanent neurological problems often occur, especially as the disease advances.
While the cause is not clear, the underlying mechanism is thought to be either destruction by the immune system or failure of the myelin-producing cells. Proposed causes for this include genetics and environmental factors such as infections. MS is usually diagnosed based on the presenting signs and symptoms and the results of supporting medical tests.
Immunologic -
MS is considered an immune-mediated disease where the immune system malfunctions and attacks the Central Nervous System. Research about which immune cells are accountable for the attack is still in progress. Scientists are also soliciting to reveal what causes these cells to strike. They’re also searching for methods to control or stop the progression of the disease.
Genetic connections -
Some genes are believed to play a key role in MS. Your chance of developing MS is slightly higher if a close relative, such as a parent or sibling, has developed the disease. According to the Multiple Sclerosis Foundation (MSF), if one parent has MS, the risk of their children getting the disease is estimated between two and five percent. Scientists believe that people with MS are born with a genetic susceptibility to react to certain (unknown) environmental agents. An autoimmune response is triggered when they encounter these agents.
Environment -
The longer the skin is bare to sunlight, the more your body naturally produces the vitamin D. Because MS is believed to be an immune-mediated disease, vitamin D and sunlight exposure may be linked. Vitamin D benefits the function of the immune system. People who live near the equator are exposed to more sunlight. As a result, their bodies produce more vitamin D.
Infections -
Researchers are contemplating the likelihood that viruses and bacteria may cause MS. Viruses are known to cause inflammation and a breakdown of myelin (called demyelination). Therefore, it’s possible that a virus will trigger MS. Various viruses and bacteria are being scrutinize to ascertain if they’re involved in the development of MS. These include:
Healthline.com
Mayoclinic.org
#stayHealthy
This damage disrupts the ability of parts of the nervous system to communicate, resulting in a wide range of signs and symptoms including physical, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. MS takes several forms, with new symptoms either...
occurring in isolated attacks (relapsing forms) or building up over time (progressive forms) Between attacks, symptoms may disappear completely; however, permanent neurological problems often occur, especially as the disease advances.
While the cause is not clear, the underlying mechanism is thought to be either destruction by the immune system or failure of the myelin-producing cells. Proposed causes for this include genetics and environmental factors such as infections. MS is usually diagnosed based on the presenting signs and symptoms and the results of supporting medical tests.
Causes
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) affects everyone differently. The extremity of the disease and the types of symptoms diverge from individual to individual. The precise cause of MS is unknown. However, scientists believe that four factors may play a role in the development of the disease, which areImmunologic -
MS is considered an immune-mediated disease where the immune system malfunctions and attacks the Central Nervous System. Research about which immune cells are accountable for the attack is still in progress. Scientists are also soliciting to reveal what causes these cells to strike. They’re also searching for methods to control or stop the progression of the disease.
Genetic connections -
Some genes are believed to play a key role in MS. Your chance of developing MS is slightly higher if a close relative, such as a parent or sibling, has developed the disease. According to the Multiple Sclerosis Foundation (MSF), if one parent has MS, the risk of their children getting the disease is estimated between two and five percent. Scientists believe that people with MS are born with a genetic susceptibility to react to certain (unknown) environmental agents. An autoimmune response is triggered when they encounter these agents.
Environment -
The longer the skin is bare to sunlight, the more your body naturally produces the vitamin D. Because MS is believed to be an immune-mediated disease, vitamin D and sunlight exposure may be linked. Vitamin D benefits the function of the immune system. People who live near the equator are exposed to more sunlight. As a result, their bodies produce more vitamin D.
Infections -
Researchers are contemplating the likelihood that viruses and bacteria may cause MS. Viruses are known to cause inflammation and a breakdown of myelin (called demyelination). Therefore, it’s possible that a virus will trigger MS. Various viruses and bacteria are being scrutinize to ascertain if they’re involved in the development of MS. These include:
- Measles
- Human herpes virus-6
- Epstein-Barr
Symptoms
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a disease with uncertain symptoms that can fluctuate in intensity eg. fatigue and numbness, severe cases can cause paralysis, vision loss, and diminished brain function.Treatment
There is no cure for multiple sclerosis. Treatment typically focuses on speeding recovery from attacks, slowing the development of the disease and controlling symptoms. Some people have such moderate symptoms that no treatment is required. The treatment for MS are :-
- Treatment for attacks which involves the use of some corticosteroids such as intravenous drugs. Plasma exchange which may also be used if the symptoms are severe and haven't responded to steroids.
- Treatment to modify progression which includes the use of beta interferon etc.
- Treatment for signs and symptoms e.g. medication to reduce fatigue, physical therapy among others
Sources: wikipedia
Healthline.com
Mayoclinic.org
#stayHealthy









0 comments:
Post a Comment
WE LOVE YOUR COMMENTS AND CONTRIBUTIONS, LETS HEAR FROM YOU...