Ebola virus is a human disease caused by the Ebola virus. It is a severe and often deadly disease that can occur in humans and animals such as primates E.g. Monkeys. Since its discovery in 1976, Ebola has become the biggest outbreak on record, recording a high mortality rate and often killing between 50%and 90% of those infected with the virus.
Ebola virus disease popularly
known as (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever, is known to be a severe, contagious
and often fatal illness in humans.
According to (WHO, 2014), EVD
outbreaks occur primarily in remote villages in central and west Africa, almost
near tropical rainforest. The virus is known to be
 Transmitted from wild animals
to people and the rate at which it spread is said to be significantly high in
human population through a method of transmission
Transmitted from wild animals
to people and the rate at which it spread is said to be significantly high in
human population through a method of transmission
Known as human-to-human.
According to research carried
out it is believed that Ebola first appeared in 1976 in 2 simultaneous
outbreaks, in Nzara, Sudan, and in Yambuku, Democratic
Republic of Congo. Then the
later was situated in a village near the EBOLA River, from which the disease
takes its name. The genus Ebolavirus is 1 of 3 members
of the Filoviridae
family (Filovirus) along with genus Marburgvirus and genus Ceuvavirus.
EBOLA SYMPTOMS
Average time between
contracting the infection and the start of symptoms is 8 to 10 days, but can
occur between 2 and 21 days
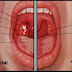
with symptoms like
- 1. sore throat,
-
- 2. fever,
-
- 3. muscle pains and
-
- 4. headache.
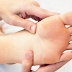
The symptoms like Nausea,
vomiting, and diarrhea follow along with decreased functioning of the liver and
kidneys.
EBOLA TRANSMISSION
The EBOLA virus can be
acquired by contact with blood and body fluids of an infected person or animal
(commonly monkeys and fruit bats), including
The embalming of an infected
dead person or by contacts with contaminated medical equipment particularly
needles and syringes. The quick onset of disease makes it
easier to identify sick
individuals and limits a person’s ability to spread the disease by traveling
to other region. Because dead bodies are still highly infectious, some doctors
dispose them off in a safe manner despite local traditional burial rights.
Medical workers who do not wear appropriate protective clothing and gloves
may also contract the
disease. It is also noted that the disease is not transmitted through
the open air. Once human infection occurs, the disease may/will spread among
people as well.
PREVENTION OF EBOLA
Prevention can be done in
many ways which includes
- Decreasing the spread of disease from infected monkeys and pigs to humans by regular checking of such animals for infection also killing and properly disposing the body (without getting exposed by touching with bare hands) if the disease is discovered.
- Properly cooking meat and wearing protective gloves when handling meat as well as wearing protective clothing and gloves when around an infected person.
- Samples of body fluids and tissues from people especially with the disease should be handled with special caution.
- According to the Centre for Disease Control and Prevention, it is important to wash your hands thoroughly with warm water and soap or, if that is not available, a hand sanitizer can be used.
- Avoid any contact with someone you believe is infected, especially with their bodily fluids, advises the World Health Organisation (WHO).
- If you need to go near someone with the virus, use protective gear such as face masks and gloves.
- Health workers in West Africa have taken full precautions, wearing protective suits that cover their entire bodies, as well as hosing down areas infected patients have used.
- WHO states any areas an infected person could have had contact with, such as bed linens, should be disinfected.
- If you believe someone you know has been infected, or if you think you might have contracted Ebola, the best thing to do is isolate yourself from any other people around you and call medical help immediately.
- A sudden temperature, muscle aches, vomiting or a rash might indicate you have the disease.
EBOLA TREATMENT
Presently no drug has been approved to treat Ebola Virus Disease . People diagnosed with Ebola receive supportive care and treatment for
complications. Scientists are coming closer to developing vaccines for
these deadly diseases. For now there is no vaccine or specific treatment for Ebola.
#HEalth is #Wealth, #stayHealthy










0 comments:
Post a Comment
WE LOVE YOUR COMMENTS AND CONTRIBUTIONS, LETS HEAR FROM YOU...